The structure of both columnar and laminar pyrolytic graphites is close to that of the ideal graphite crystal. These graphites have a high degree of preferred crystallite alignment particularly after heat-treatment, and their properties tend to be anisotropic. Melting poind, sublimation point, heat of vaporization, entropy, enthalpy, specific heat, and chemical properties are similar to that of the single-crystal graphite but other properties may vary significantly.
The properties of pyrolytic graphite are summarized in Table 7.2. The values listed were collected from the manufacturer’s data sheets. The spread in value may represent slightly different materials and differences in the degree of graphitization. It may also reflect variations in the test methods; for instance, the measurement of mechanical properties may vary widely depending on the sample geometry and the test method.
Table 7.2 Properties of oriented pyrolytic graphite at 25C.
| Density, g/cm3 | 2.10-2.24 |
| Flexural strength tested in the c direction, Mpa | 80-170 |
| Tensile strength tested in the ab directions, Mpa | 110 |
| Young’s modulus of elasticity, Gpa | 28-31 |
| Thermal conductivity, W/m.K
C direction ab directions |
1-3 190-390 |
| Thermal expansion 0-100C, *10-6/m.K
c direction ab directions |
15-25 -1 to 1 |
| Electrical resistivity, μΩ.m
c direction ab directions |
1000-3000 4-5 |
Mechanical properties: The mechanical properties of pyrolytic graphite are like those of the ideal graphite crystal in the sense that they show a marked increase with increasing temperature as shown in Fig.7.9. Above 2600C, the strength drops sharply.
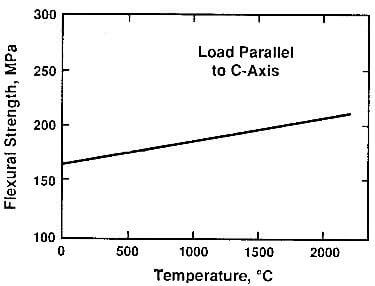
fig.7.9-flexural strength of pyrolytic graphite as a function of temperature.
Thermal conductivity: The thermal conductivity of the ideal graphite crystal in the ab directions is high. It is far lower for the average pyrolytic graphite but still high enough for the material to be considered a good thermal conductor, similar to copper.
The thermal conductivity in the c direction is approximately 2.0 W/m.K at 25C and, in this direction, graphite is a good thermal insulator, comparable to most plastics. The anisotropy ratio is approximately 200.
The thermal conductivity in both the ab and c directions decreases with temperature.
Thermal expansion: The thermal expansion of pyrolytic graphite, like that of the ideal graphite crystal, has a marked anisotropy. It is low in the ab directions but an order of magnitude higher in the c direction.
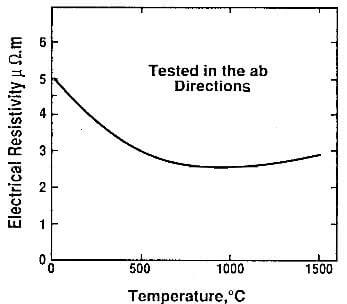
fig.7.11-electrical resistivity of pyrolytic graphite as a function of temperature
Electrical properties: The electrical properties of pyrolytic graphite also reflect the anisotropy of the material and there is a considerable difference between the resistivity in the ab and the c directions. Pyrolytic graphite is considered to be a good electrical conductor in the ab directions, and an insulator in the c direction. Its electrical resistivity varies with temperature as shwon in Fig.7.11.